deep-learning
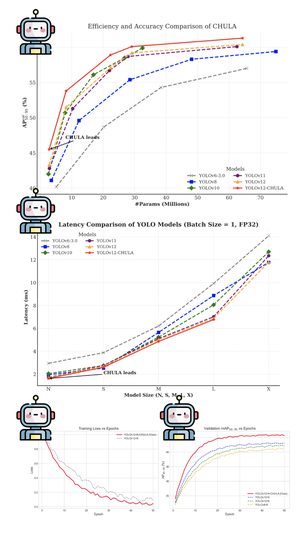
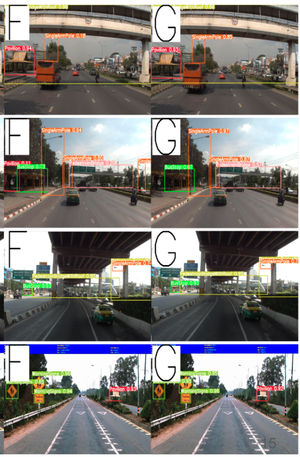
Accurately segmenting land boundaries from Thai land title deeds is crucial for reliable land management and legal processes, but remains challenging due to low-quality scans, diverse layouts, and complex overlapping elements in documents. Existing methods often struggle with these difficulties, resulting in imprecise delineations that can cause disputes or inefficiencies. To address these issues, we propose CHULA, a novel Custom Heuristic Uncertainty-guided Loss tailored specifically for robust land title deed segmentation. CHULA uniquely combines domain-specific heuristic priors with uncertainty modeling in a unified loss function that effectively guides the model to focus on clearer regions while refining boundaries and suppressing noisy areas. Evaluated on a carefully curated Thai Land Title Deed Dataset, CHULA achieves an impressive 92.4% accuracy, significantly surpassing standard segmentation baselines. Our results highlight the promise of integrating uncertainty and heuristic knowledge to enhance segmentation accuracy in complex, real-world documents. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/kaopanboonyuen/CHULA.
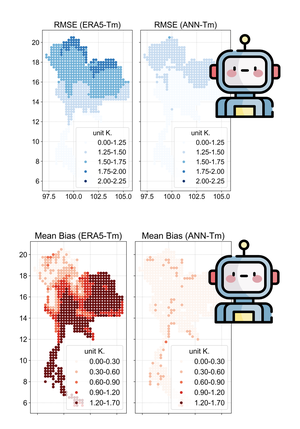
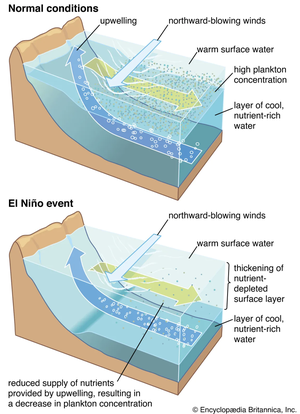
Forecasting sea surface currents is essential for applications such as maritime navigation, environmental monitoring, and climate analysis, particularly in regions like the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman Sea. This paper introduces SEA-ViT, an advanced deep learning model that integrates Vision Transformer (ViT) with bidirectional Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) to capture spatio-temporal covariance for predicting sea surface currents (U, V) using high-frequency radar (HF) data. The name SEA-ViT is derived from Sea Surface Currents Forecasting using Vision Transformer, highlighting the model’s emphasis on ocean dynamics and its use of the ViT architecture to enhance forecasting capabilities. SEA-ViT is designed to unravel complex dependencies by leveraging a rich dataset spanning over 30 years and incorporating ENSO indices (El Niño, La Niña, and neutral phases) to address the intricate relationship between geographic coordinates and climatic variations. This development enhances the predictive capabilities for sea surface currents, supporting the efforts of the Geo-Informatics and Space Technology Development Agency (GISTDA) in Thailand’s maritime regions. The code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/kaopanboonyuen/gistda-ai-sea-surface-currents.