DOTA: Deformable Optimized Transformer Architecture for End-to-End Text Recognition with Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Abstract
Text recognition in natural images remains a highly complex yet vital challenge, with wide-ranging applications in computer vision and natural language processing. In this paper, we present a novel end-to-end framework that integrates ResNet and Vision Transformer (ViT) backbones with cutting-edge techniques such as Deformable Convolutions, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and Conditional Random Fields (CRF). These innovations work together to significantly improve feature representation and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) performance. By replacing the standard convolution layers in the third and fourth blocks with Deformable Convolutions, the framework adapts more flexibly to complex text layouts, while adaptive dropout helps prevent overfitting and enhance generalization. Moreover, incorporating CRFs refines the sequence modeling for more accurate text recognition. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets—IC13, IC15, SVT, IIIT5K, SVTP, and CUTE80—demonstrate the framework’s exceptional performance, achieving remarkable accuracies of 97.32% on IC13, 58.26% on IC15, 88.10% on SVT, 74.13% on IIIT5K, 82.17% on SVTP, and 66.67% on CUTE80, yielding an average accuracy of 77.77%. These results establish a new state-of-the-art for text recognition, showing the robustness of our approach across diverse and challenging datasets. Our method represents a significant leap forward in OCR technology, addressing challenges in recognizing text with various distortions, fonts, and orientations. The framework has proven not only effective in controlled conditions but also adaptable to more complex, real-world scenarios. The code for this framework is available at https://github.com/kaopanboonyuen/DOTA.
DOTA: Deformable Optimized Transformer Architecture for End-to-End Text Recognition with Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Abstract
Text recognition in natural images remains one of the most challenging yet essential tasks within the fields of computer vision and natural language processing. With applications ranging from document digitization to autonomous navigation, effective text recognition is more critical than ever before. In this paper, we introduce DOTA, a novel end-to-end framework that combines ResNet and Vision Transformer (ViT) backbones with advanced methodologies such as Deformable Convolutions, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and Conditional Random Fields (CRF) to significantly enhance Optical Character Recognition (OCR) performance.

At the heart of DOTA is a revolutionary approach where traditional convolution layers in the third and fourth blocks of the network are replaced with Deformable Convolutions—a technique that offers adaptive and robust feature extraction, making it ideal for recognizing text in complex and irregular layouts. Furthermore, adaptive dropout is integrated to ensure regularization, helping to prevent overfitting and boosting generalization. To refine the sequential modeling of text, we leverage CRFs, which excel in capturing intricate dependencies inherent in text recognition tasks.
We conducted extensive experiments on six benchmark OCR datasets—IC13, IC15, SVT, IIIT5K, SVTP, and CUTE80. Our results demonstrate the exceptional performance of DOTA, achieving remarkable accuracies:
- IC13: 97.32%
- IC15: 58.26%
- SVT: 88.10%
- IIIT5K: 74.13%
- SVTP: 82.17%
- CUTE80: 66.67%
This gives us an average accuracy of 77.77%, setting a new state-of-the-art in the field of text recognition. The results clearly highlight the robustness of DOTA across a variety of challenging datasets.
Introduction
Text recognition from images has long been a challenging problem, with significant implications for applications in document processing, automated data entry, and even autonomous systems. With traditional Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems heavily relying on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), we’ve seen progress in extracting features from images. However, as text layouts become more complex—such as when dealing with varying fonts, orientations, and complex backgrounds—CNNs often fall short. Enter the Transformer architectures: these models have revolutionized many areas in computer vision, particularly in handling long-range dependencies through their self-attention mechanisms, offering significant improvements for text recognition tasks.
While Transformer-based models have pushed the boundaries of OCR performance, there is still a need for further improvements, especially in the area of feature extraction and sequence modeling. That’s where DOTA comes in. By combining the strengths of ResNet and Vision Transformer (ViT) backbones, this novel approach leverages Deformable Convolutions, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and Conditional Random Fields (CRF) to achieve new levels of OCR accuracy.
The DOTA Framework
The architecture of DOTA is designed to enhance both feature extraction and sequence modeling, key areas in text recognition:
-
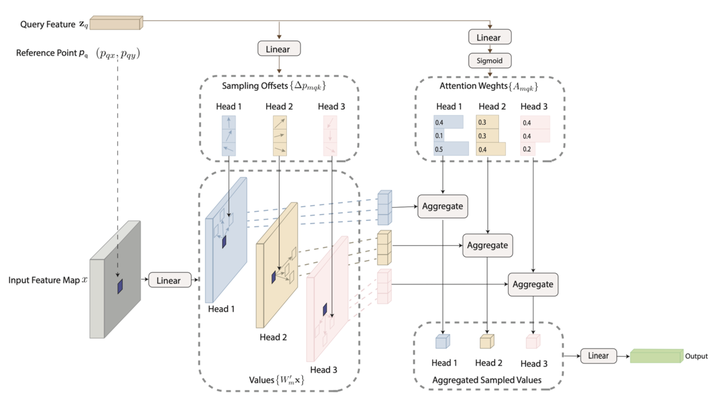
Deformable Convolutions: By replacing standard convolutions in the network’s third and fourth blocks with Deformable Convolutions, we allow for more flexible and adaptive feature extraction. This helps capture irregular text patterns and varying layouts more effectively.
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation: The integration of this approach provides context-aware enhancements, further refining the recognition process.
-
Conditional Random Fields (CRFs): CRFs have been incorporated into the framework to better model the sequential nature of text, providing the necessary context to improve recognition accuracy, especially for more complex sequences of characters.
Together, these components form the backbone of DOTA, providing a more robust, adaptable, and precise model for OCR tasks. The effectiveness of DOTA is clearly demonstrated in its impressive performance across several standard OCR benchmark datasets.
Experimental Results
We evaluated DOTA using six widely-used OCR benchmark datasets:
- IC13: 97.32%
- IC15: 58.26%
- SVT: 88.10%
- IIIT5K: 74.13%
- SVTP: 82.17%
- CUTE80: 66.67%
With an average accuracy of 77.77%, DOTA has set a new state-of-the-art in OCR performance. The results show that the combination of Deformable Convolutions, Vision Transformers, and CRFs significantly improves recognition, even in challenging conditions where traditional methods struggle.
Conclusion
The DOTA framework represents a major leap forward in the field of text recognition. By effectively combining ResNet and Vision Transformer backbones with advanced techniques like Deformable Convolutions, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and Conditional Random Fields, it achieves impressive accuracy across a variety of challenging datasets. This work sets a new benchmark for OCR performance, providing a powerful tool for tackling the complexities of text recognition in real-world scenarios.
With this new approach, we’ve laid the foundation for even more accurate and robust text recognition systems, paving the way for smarter applications in everything from document processing to autonomous navigation.